[OS] Chapter 10 — File System Interface
File Concept
File 也是抽像的概念。
Physical storage unit in disk

File attributes (Metadata)
- Identifier: non-human-readable name
- Name
- Type
- Location
- Size
- Protection
- Last-access time, Last-updated time
File operations
- Create
- Write
- Read
- Repositioning within a file (i.e. file seek)
- Delete
- Truncating → 切掉尾巴
- Appending → 貼在尾巴
Open-File Tables
注意他存的是 metadata,不是 data
- Per-process table
Tracking all files opened by this process
跟操作這個 file 有關的資訊(independent 的)
File pointer → process 操作這個檔案到的位置
裡面還有一個 pointer 指到 file 的 System-wide table
⇒ 這樣就可以避免資料一致性的問題,所以才不要 duplicate 一份到 Per-process table 裡面
- System-wide table ****
- 不管誰操作都要看到的資訊(share 的)
- File size, disk location
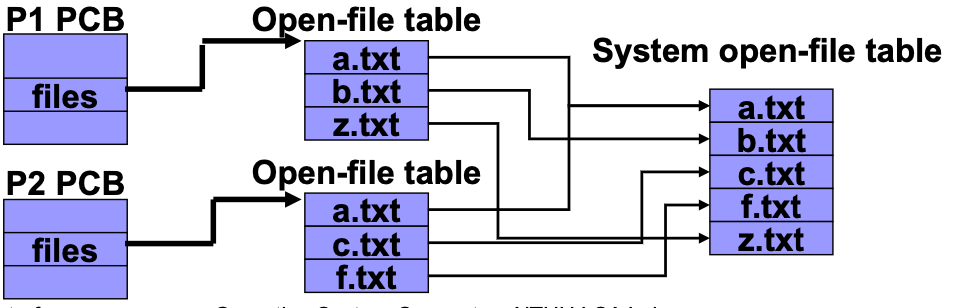
- Per-process table
Open File Attributes
- File pointer (per-process)
- File open count (system table)
- Disk location (system table)
- Access rights (per-process)
File types
.exe, .com, .obj, .cc, .mov, etc
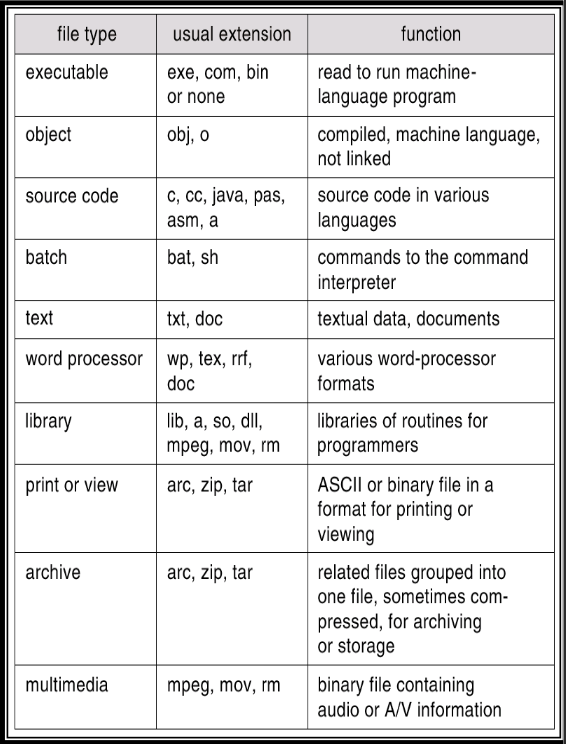
Hint for OS to operate file in a reasonable way
Access Methods
是以使用者的角度來看:
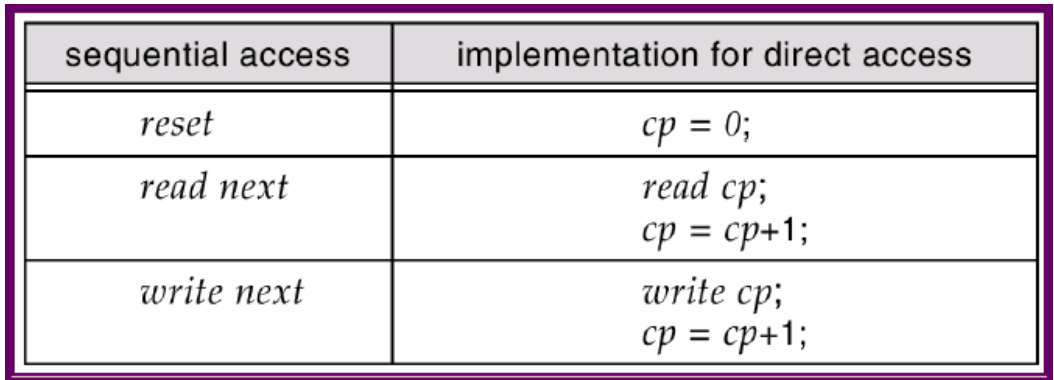
Sequential access
- 連續的存取
fread,fwrite
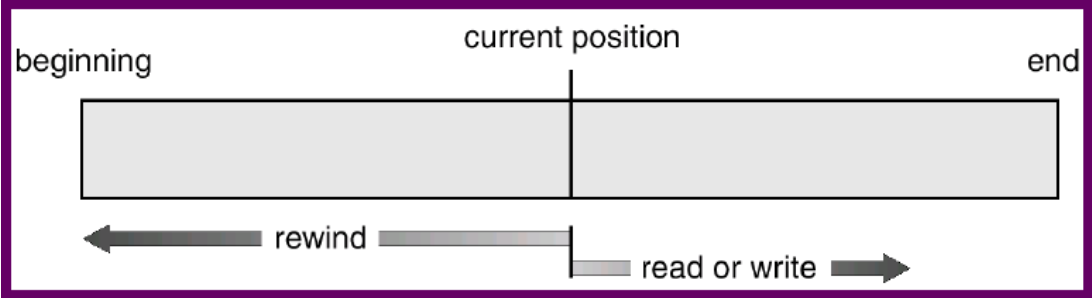
Direct (relative) access a.k.a random access
- Call API 需要給他位址
- 像是使用 table
- 使用者要自己維護位址(With great power comes great responsibility)
- Index Access Methods
DB
用 index 去存取資料
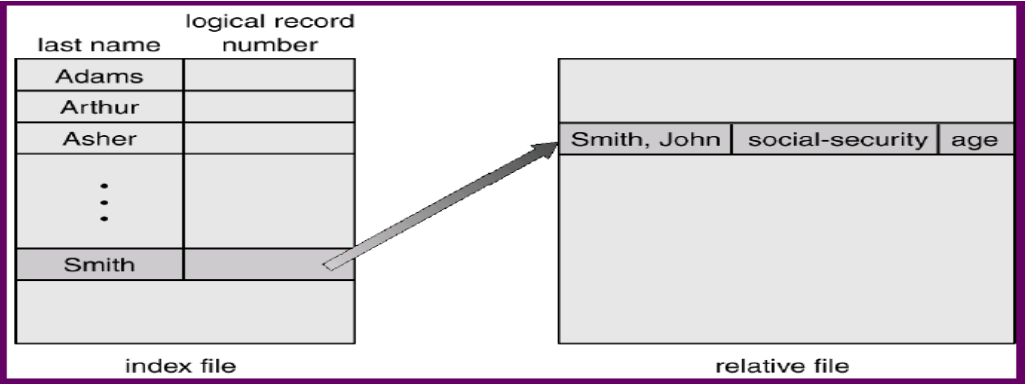
Index: contains pointers to blocks of a file
With a large file → index could become too large
To find a record in a file:
- search the index file → find the pointer
- use the pointer to directly access the record
Review Slides (I)
- File vs. Sector, Track
- Open-file (in-memory) attributes
- Per-process, system-wide?
- File-access methods?
- Sequential access
- Direct access
- Index access
Directory Structure
Directory Basics
Partition (Raw partition) — 儲存的空間切割後變成單獨的 partition 作是使用和管理,但是這個區塊我們還沒作格式化的動作
Volume — 我們有把他作 formatted(File system 的格式化) 的動作了(File system 的專有名詞)→ 強調這是由 file system 管理使用的空間
Directories — used by file system to store the information about the files in the partition
File-System Organization
File name 本身也是 directory 的一部分
- 因為要找到 file,就要有 file name
- 所以 Directory 的最後一層是 file name
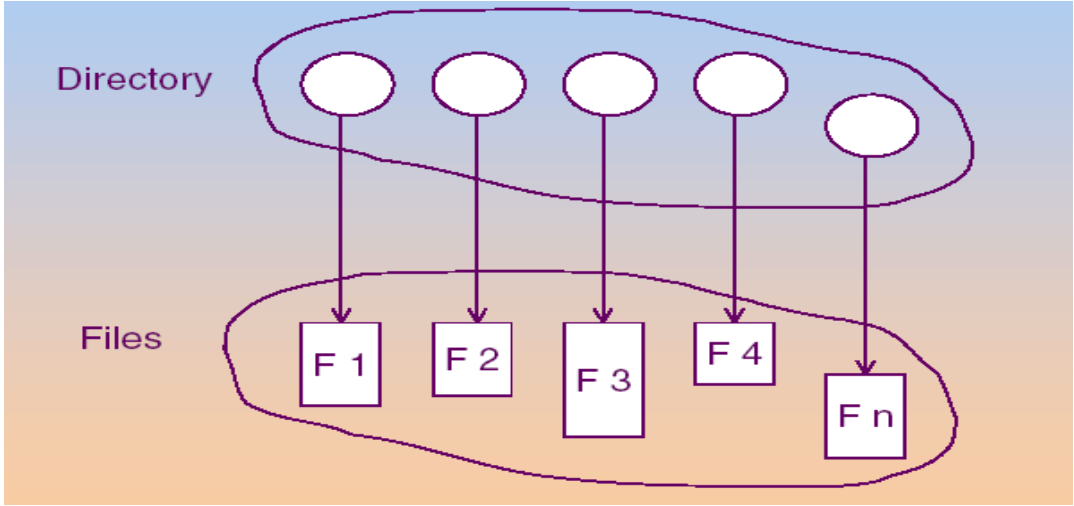
Directory Operations
- Search for a file
- Create a file
- Delete a file
- List a directory
- Rename a file
- Traverse the file system
Directory structure
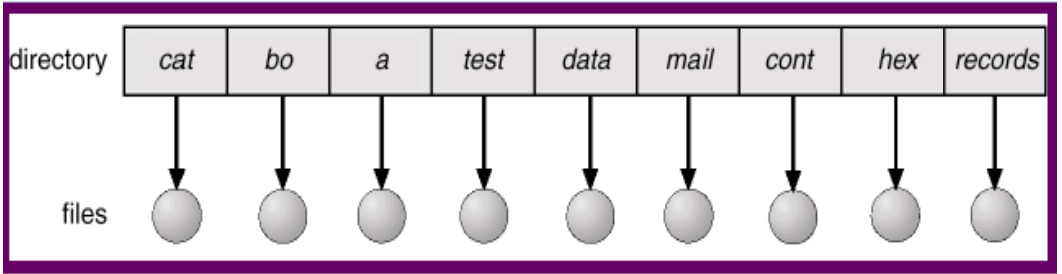
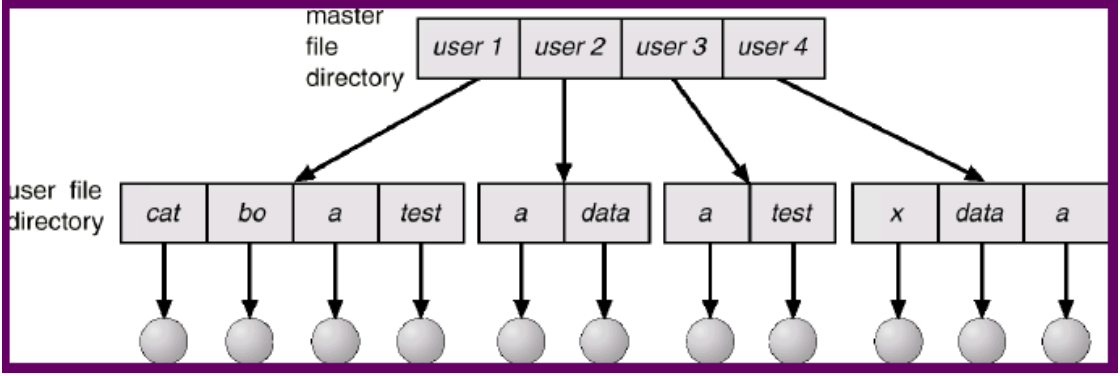
Single-Level Directory
- 指的是沒有資料夾,完全只有檔案
- Single 指的是 file name
- File name 很容易打架,因為不能重複
- 因為是 flat 的,所以每次都要 scan through,效能差
Two-Level Directory
- 出現了資料夾
- 一個 user 一個資料夾,所以還是有上面的問題
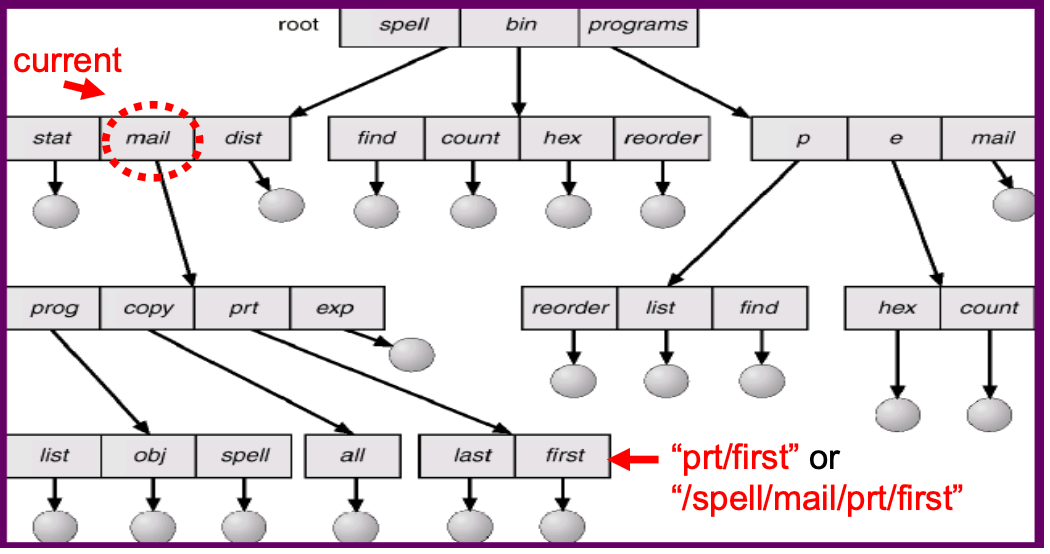
Tree-Structured Directory
- Multi-Level
- 有 absolute path 和 relative path
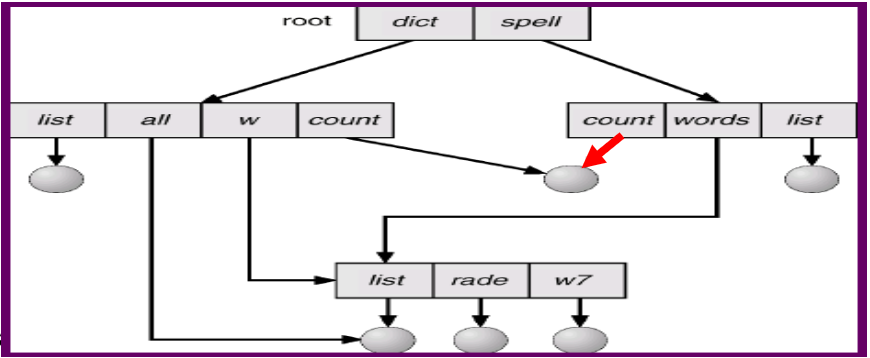
Acyclic-Graph Directory
- 可以建立捷徑到同一個 file
- When does a file actually get deleted?
- deleting the link but not the file
- deleting the file but leaves the link → dangling pointer
General-Graph Directory
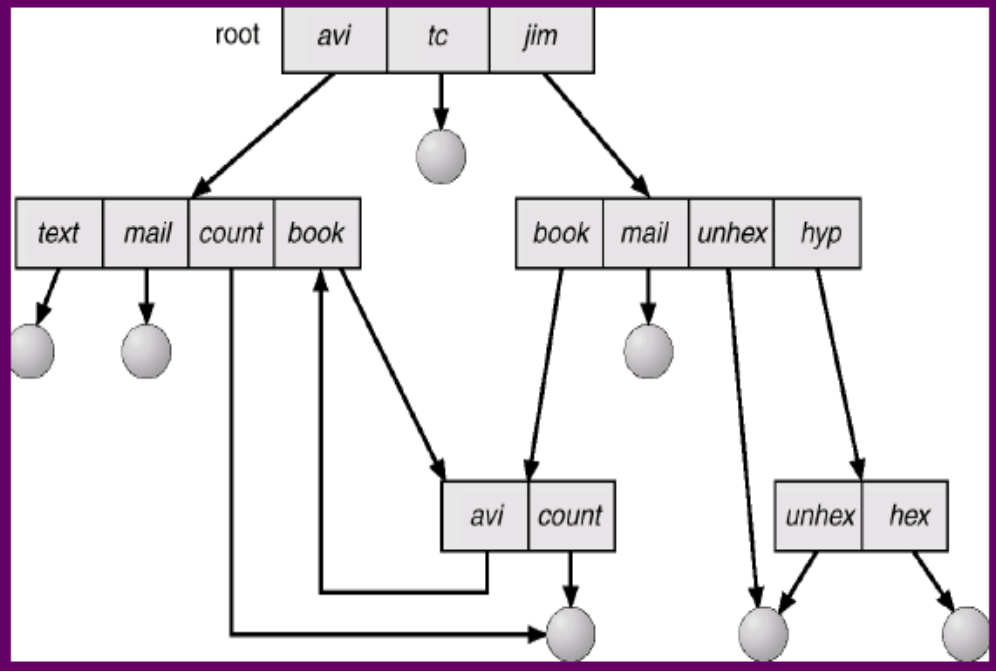
可以隨便亂指,甚至可以有 cycle
有可能會明明 access 不到了,但是因為有 link 在,所以也沒刪掉檔案
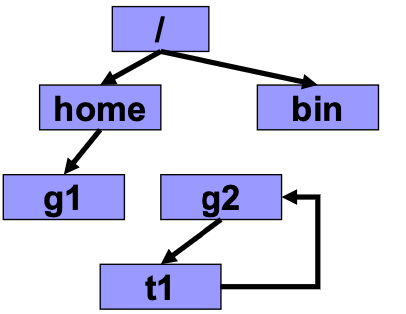
Garbage collection
→ 從 root 開始 traverse,mark 每一個人,沒 mark 到的就刪掉
☹️ Poor performance
Use cycle-detection algorithm when a link is created
Review Slides (II)
- Directory structure: pros & cons
- One-level directory
- Two-level directory
- Tree-structured directory
- Acyclic-graph directory
- General-graph directory
File System Mounting & File Sharing
Mounting
A file system must be mounted before it can be accessed
Mount point — 接到的位址(the root path that a FS will be mounted to),系統槽就是 mount 在
/Mount timing: three possibility
- boot time (系統槽)
- automatically at run-time(USB)
- manually at run-time
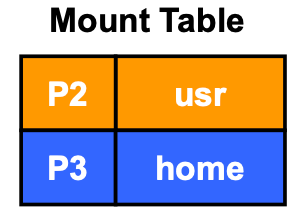
File System Mounting Example
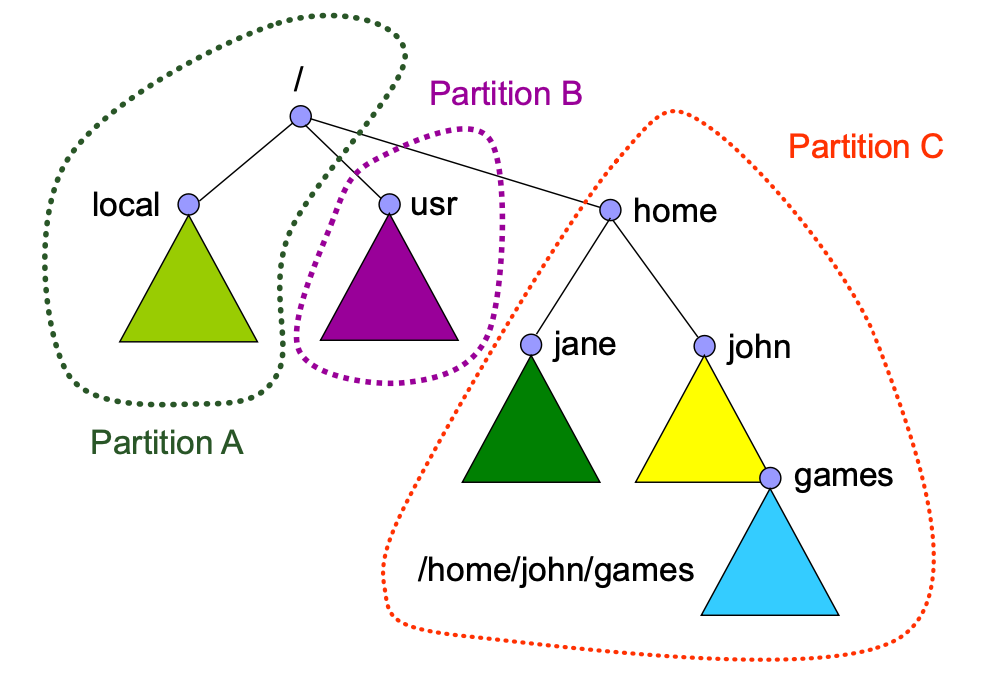
- Partition B 的 mount point 是在
/usr - Partition C 的 mount point 是在
/home
- Partition B 的 mount point 是在
mount –t ext2 /dev/sda0 /mnt/hdd- mount 一個 file type 是
ext2的(所以知道這是啥 FS,才能正確讀取),他現在是/dev/sda0(是被 I/O device attach 成一個檔案的,mount 之後才可以讀取)要 mount 到/mnt/hdd
- mount 一個 file type 是
How to extend the tree
Tree 長這樣
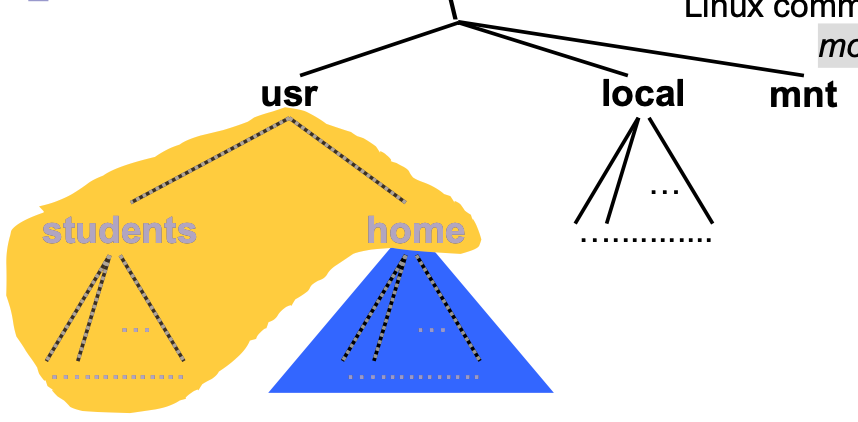
前面的
m代表那不是我管的,是 mount 進來的,所以要去查下面的 mount table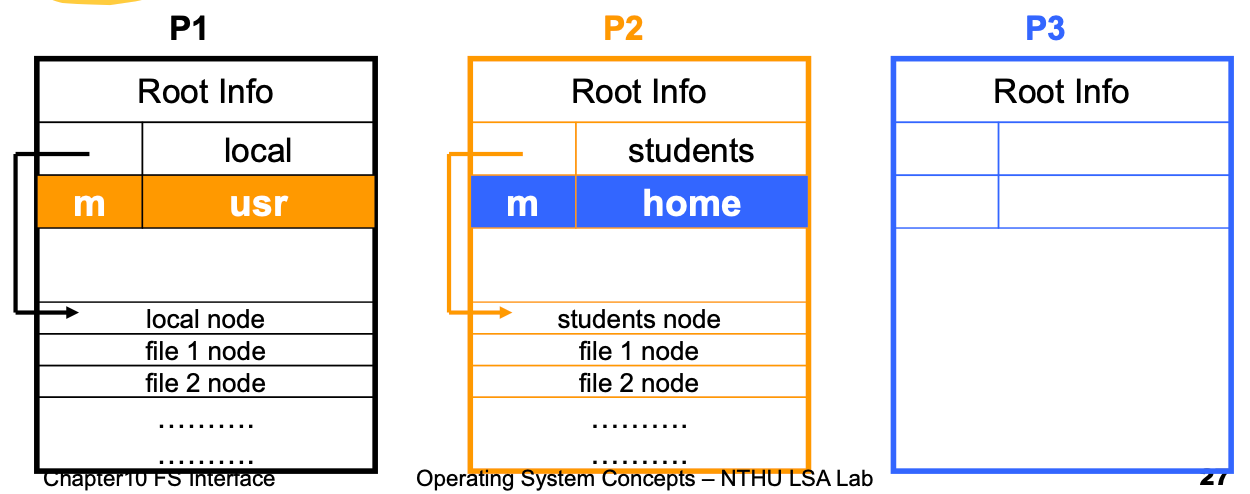
mount 就會修改這裡面的內容
Sharing
基本上都是 multi-user,所以要 sharing,但是要處理 permission
對於每一個 process,需要去管理他的
- Identity:誰 call 的(Login 就知道了)(也有 groping 去幫助管理)
- Permission:知道是誰後要知道他可以動誰
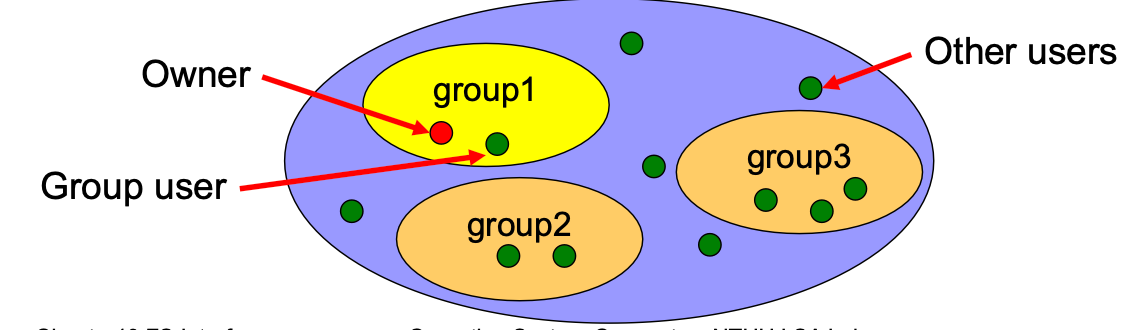
Each user — UserID, GroupID
Each file has 3 sets of attributes — owner (one and only), group (can operate), others
Access-Control
Create an access-control list (ACL) for each user
- 每次 request 就去查他的權限
☹️ 會太大,每新增一個 user or file ACL will be huger
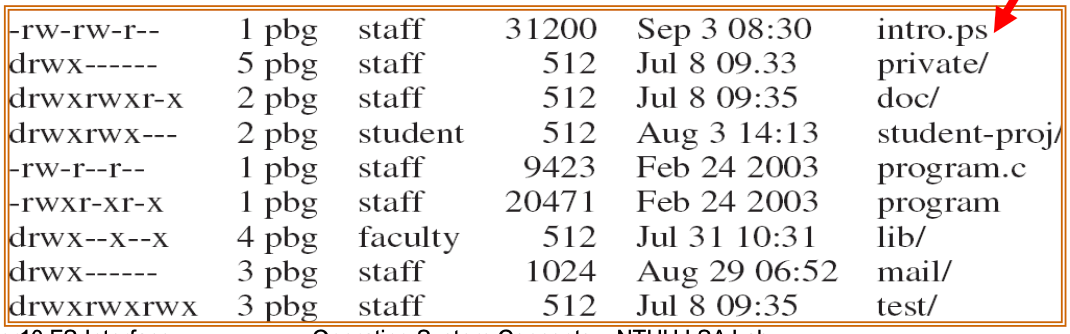
- 3 classes of users → 3 ACL (RWX) for each file
- Owner — (e.g. 7 = RWX = 111)
- group — (e.g. 6 = RWX = 110)
- other (public) — (e.g. 4 = RWX = 100)
Protection
- Access control protection
- Data failure protection
- 用加密的方式保護他不會遺失
Review Slides (III)
- File system mounting point, timing?
- Access-control list? How does it function?
Textbook Problem Set

此筆記為清華大學周志遠教授作業系統之課堂筆記,所有內容及圖片皆取材於課堂內容。
如內容有誤,歡迎來信 mail@arui.dev。